Dogs have adapted to diverse climates and terrains over thousands of years, from the snowy Arctic tundras to the dense, humid tropics. However, certain breeds are naturally suited to colder climates and may struggle in warmer, tropical environments. Factors such as physical adaptations, breed origins, behavior, and even genetic traits play significant roles in determining a dog’s climate compatibility. This article explores why some dogs are better suited for cold climates than tropical ones, highlighting the unique characteristics that enable them to thrive in the cold.
Physical Adaptations: Built for the Cold
One of the primary reasons some dogs fare better in cold climates is due to their physical adaptations, which are specially designed for retaining heat and enduring low temperatures.
Thick Fur Coats
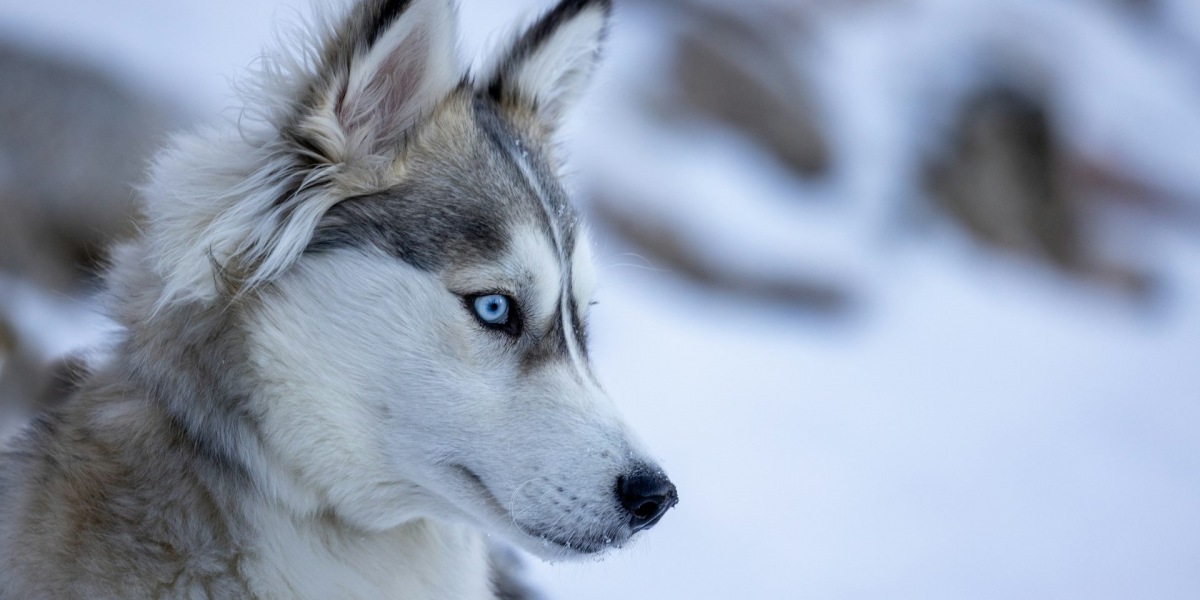
Many cold-weather breeds, such as Huskies, Malamutes, and Samoyeds, have double-layered fur coats that provide superior insulation. These coats consist of a dense underlayer that traps warm air close to the skin and an outer layer that repels moisture and protects against the wind. This fur design keeps cold-weather dogs warm and comfortable even in freezing temperatures, but it can make them uncomfortable or even prone to overheating in warm, humid climates where their bodies can’t dissipate heat as effectively.
Body Fat Composition
Dogs adapted to cold environments often have a higher body fat percentage, which acts as an additional layer of insulation against the cold. This fat layer not only helps conserve heat but also provides stored energy during cold periods, especially in environments where food may be scarce. This natural insulation becomes a disadvantage in tropical climates, where thicker body fat may hinder a dog’s ability to cool down, making them more susceptible to overheating.
Compact Body Shape
Many cold-weather breeds have compact, stocky builds with shorter legs and broader bodies. This body structure reduces the surface area exposed to cold air, helping them retain body heat more efficiently. Conversely, long, slender bodies are better suited for heat dissipation, which is why you’re more likely to see slim, agile breeds in warmer regions. Compact, muscular dogs like the Saint Bernard or Newfoundland, however, are better adapted to cold temperatures than tropical heat.
Breed Origins: Evolution and Climate-Specific Adaptations
The evolutionary history of certain dog breeds plays a significant role in their ability to adapt to cold environments. Many breeds were developed in specific climates, leading to distinct adaptations that are passed down through generations.
Arctic Breeds
Arctic breeds, including the Siberian Husky, Alaskan Malamute, and Greenland Dog, evolved in some of the coldest regions on Earth, where temperatures regularly drop well below freezing. These dogs are not only accustomed to the cold but rely on it to maintain a comfortable body temperature during intense physical activity. Arctic breeds have unique physical and behavioral traits that help them thrive in extreme cold, such as high endurance and a strong work ethic, but these traits make them uncomfortable in warmer environments.
Mountain Breeds
Mountain breeds, like the Saint Bernard, Bernese Mountain Dog, and Tibetan Mastiff, are built to endure the cold, high-altitude climates of mountainous regions. Their heavy coats and robust physiques make them adept at dealing with harsh winds and snowy conditions. However, these very adaptations make it difficult for them to thrive in hot, humid climates. The heavy coats and thick fur necessary for protecting them from freezing temperatures can lead to overheating in tropical environments.
Temperate Breeds
Some breeds, while not adapted to extreme cold, do well in temperate climates with mild seasonal changes. These breeds, such as the Border Collie or Golden Retriever, are versatile and can tolerate colder weather due to moderate fur coats and resilience, but they may struggle in high heat and humidity. Temperate breeds are more adaptable, but even they can experience discomfort or health risks if exposed to extreme temperatures outside their tolerance range.
Behavioral and Physiological Factors: Responses to Temperature and Activity
Beyond physical adaptations, cold-weather dogs exhibit specific behaviors and physiological traits that align with colder climates, which can make warmer climates challenging for them.
Lower Heat Tolerance
Cold-adapted breeds have a lower heat tolerance, which means they struggle to regulate their body temperature in warm, humid conditions. Unlike tropical breeds that are efficient at dissipating heat, cold-weather dogs retain heat, which can lead to quick overheating in tropical environments. This low heat tolerance also affects their activity levels; cold-adapted dogs may be less energetic and more prone to lethargy in hot weather as they try to avoid excessive heat exposure.
Higher Activity Levels in Cold
Cold-climate breeds, particularly working dogs, have high energy levels and require regular exercise. The cold helps keep them cool during physical activities, allowing them to sustain high energy outputs without the risk of overheating. In warm climates, however, this natural tendency for activity can be risky, as high-intensity play or exercise may lead to dehydration or heat exhaustion more quickly. Owners in warmer climates must often restrict activity to early mornings or late evenings, which may not fully meet the exercise needs of these active breeds.
Resting and Energy Conservation
Cold-weather dogs have adapted to conserve energy in colder conditions, often showing behaviors such as curling up tightly to retain body heat or seeking shelter from wind and snow. These behaviors are beneficial in cold climates but may not serve the same purpose in tropical environments. Additionally, energy conservation tendencies can become counterproductive in warm climates, as lower activity levels can lead to weight gain if exercise is limited to avoid overheating.
Health and Survival Considerations: Risks in Hot Climates
In warm climates, cold-weather dogs are at increased risk for specific health issues. Their thick coats, low heat tolerance, and natural behaviors make them vulnerable to heat-related problems when they’re in tropical or warm environments.
Skin and Coat Health
In tropical climates, a thick double coat can trap moisture, leading to issues like skin infections and hot spots. The fur may retain water from humidity, sweat, or even swimming, creating an environment conducive to bacterial growth. Regular grooming and proper care can help, but some cold-weather dogs may still experience skin irritation and discomfort due to their dense coats in warm conditions.
Risk of Heat Stroke
Heat stroke is a severe concern for cold-adapted breeds in hot environments. Dogs regulate body temperature through panting, but thick-coated dogs are less effective at dissipating heat. In hot weather, even minimal exercise can elevate body temperatures to dangerous levels, making heat stroke a real risk. Owners of cold-weather breeds in warm climates must closely monitor their dogs and avoid physical exertion during the hottest parts of the day.
Dehydration Risks in Heat
Cold-weather breeds are often less adept at drinking water frequently to cool down, making them more susceptible to dehydration in warm climates. These dogs may not instinctively seek water as often as tropical breeds, leading to increased risks of dehydration. Hydration is essential for temperature regulation, and in tropical climates, it’s critical for owners to encourage cold-weather breeds to drink regularly, especially after physical activity.
Genetic and Evolutionary Traits: Specific Traits for Cold-Weather Survival
Finally, the genetics of cold-weather breeds offer clues as to why these dogs are suited for the cold and face challenges in warmer climates.
Thick Undercoats
Many cold-weather breeds have thick undercoats that trap warm air close to their bodies, providing necessary insulation in freezing temperatures. This same undercoat becomes problematic in warm climates, as it traps heat and reduces airflow, making it challenging for the dog to cool down effectively. While regular grooming can help reduce the density of the undercoat, it doesn’t fully alleviate the issues caused by this adaptation in hot weather.
Energy Expenditure Patterns
Cold-weather breeds are adapted to conserve energy during harsh winters, which influences their metabolic rates and energy requirements. Their metabolism is suited for cold temperatures, where extra energy is needed to stay warm. In warm climates, however, their slower metabolism and tendency to conserve energy may lead to weight gain, as they are less active and expend less energy.
Paws and Pads Adapted for Cold
Cold-weather breeds often have fur-covered or thickly padded paws that provide protection against ice and snow. While these adaptations are beneficial in cold environments, they may cause discomfort on hot surfaces in tropical climates. Walking on warm pavement or sand can be challenging for these dogs, as their pads aren’t adapted to tolerate heat.
The unique physical, behavioral, and genetic traits of cold-weather dogs make them perfectly suited to frigid climates but present challenges in tropical environments. Understanding these adaptations helps pet owners better manage their dogs’ needs and ensures a comfortable and healthy environment. By recognizing the needs and limitations of cold-adapted breeds, we can provide them with the care and lifestyle that best supports their well-being, regardless of the climate.