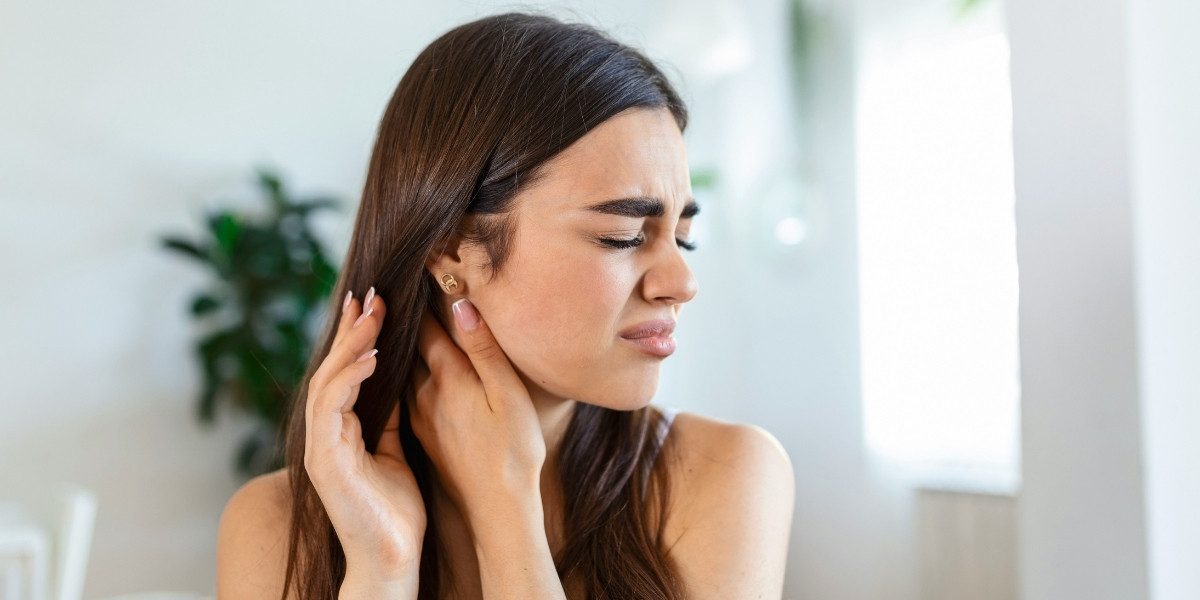
Contact dermatitis is a widespread skin condition resulting from direct exposure to irritants or allergens. It causes inflammation that often leads to redness, itching, and discomfort, significantly impacting everyday life. While it might appear straightforward, preventing contact dermatitis requires a detailed understanding of its triggers and a multifaceted approach to protecting the skin. By adopting comprehensive strategies, individuals can safeguard their skin, minimize flare-ups, and maintain a healthy barrier that resists irritation.
Read Also: Autoimmune Diseases: From Cells to Holistic Care
What Are the Causes and Types of Contact Dermatitis?
Contact dermatitis is broadly divided into two types: irritant contact dermatitis and allergic contact dermatitis. Irritant contact dermatitis occurs when substances directly damage the skin’s outer layer. This damage can happen after repeated exposure to harsh chemicals like detergents, solvents, or even water. The skin’s natural oils get stripped away, leaving it dry, cracked, and vulnerable. Allergic contact dermatitis, on the other hand, is an immune system reaction triggered by allergens. These allergens are substances that provoke sensitivity after initial exposure, such as nickel, fragrances, preservatives, or plants like poison ivy. Unlike irritants, allergens don’t cause immediate damage but activate a hypersensitive immune response that leads to redness, swelling, and itching.
Understanding the specific cause is vital because the approaches to prevention and treatment can differ. Both forms, however, share the risk of worsening if the skin’s barrier is compromised or if exposure continues unchecked. Preventing contact dermatitis starts with identifying the substances that provoke skin reactions. Keeping a diary of products used, environments encountered, and any skin symptoms that arise can help pinpoint potential irritants or allergens. Patch testing under medical supervision can provide definitive identification of allergens, especially when the cause is unclear.
Once identified, minimizing exposure is the most effective preventive measure. This may involve reading labels carefully to avoid known irritants in soaps, detergents, cosmetics, and cleaning agents. Switching to fragrance-free or hypoallergenic products is a wise choice, as these tend to be less harsh on sensitive skin. In work environments, particularly in industries like healthcare, manufacturing, or cleaning, protective gear such as gloves, aprons, and barrier creams should be standard. Avoiding prolonged contact with water and chemicals can significantly reduce risk.
What Role Does Proper Skin Care Play in Prevention?
Maintaining a robust skin barrier is crucial for preventing dermatitis. The skin’s barrier protects against external aggressors and maintains moisture. When damaged, the skin becomes prone to irritation and allergic reactions. Moisturizing regularly helps restore and maintain this barrier. Emollients that contain ceramides, glycerin, or natural oils support hydration and skin repair. Applying moisturizers immediately after washing or bathing seals in moisture and counteracts dryness caused by water exposure. Using mild, pH-balanced cleansers instead of harsh soaps minimizes irritation. Lukewarm water is preferable to hot water, which strips oils and exacerbates dryness. Avoiding abrasive scrubbing preserves the skin’s natural defenses.
Barrier creams can be applied before exposure to irritants, adding an extra layer of protection. Choosing creams designed for sensitive skin ensures they don’t introduce new allergens. Occupational contact dermatitis is a significant concern in many industries. Employers have a responsibility to create safe work environments that reduce the risk of skin conditions.
This involves providing training on hazard recognition and proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE). Gloves should fit well and be made of materials that don’t cause allergic reactions themselves. Encouraging workers to take breaks from exposure and providing hand care stations with gentle cleansers and moisturizers support skin health. Substituting less harmful substances for known irritants and improving ventilation reduce airborne risks. Employers should encourage early reporting of skin issues so interventions can occur before conditions worsen. A culture of awareness and prevention benefits both employees and organizations by reducing absenteeism and healthcare costs.
What Lifestyle Choices Help Protect Against Contact Dermatitis?
Simple lifestyle changes can make a big difference in reducing dermatitis risk. Wearing loose, breathable clothing helps reduce sweat buildup, which can irritate the skin. Choosing natural fabrics like cotton instead of synthetic materials avoids unnecessary friction and allergies. Managing stress is another key factor. Stress weakens immune function and can exacerbate inflammatory skin conditions. Practicing relaxation techniques, getting sufficient sleep, and engaging in physical activity promote overall skin and immune health. Adequate hydration and a balanced diet rich in vitamins and antioxidants support skin repair and resilience. Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption further protects skin integrity.
If symptoms of contact dermatitis persist despite preventive efforts, professional consultation is essential. Dermatologists can perform patch testing to identify allergens precisely. They may also recommend topical steroids or other medications to reduce inflammation during flare-ups. Early diagnosis prevents complications such as secondary infections or chronic skin thickening. Medical advice ensures that prevention strategies are tailored to individual needs and that any underlying conditions are addressed. Ongoing medical support helps manage dermatitis proactively rather than reactively, improving quality of life.
Read Also: Health and Wellness Trends: The Future of Well-Being
What Emerging Treatments and Research Offer Hope?
Recent advances in dermatological research focus on enhancing the skin’s barrier function and modulating immune responses. New topical formulations aim to repair skin damage more effectively and reduce sensitivity. Research into personalized skincare, considering genetic and environmental factors, promises more targeted prevention. Immunomodulatory therapies may provide relief for those with severe allergic contact dermatitis. Educational campaigns and digital tools increase public awareness, promoting healthier habits and earlier intervention. Collaboration between researchers, clinicians, and industry supports innovation and practical solutions.
Public health initiatives that educate about contact dermatitis risks and prevention are vital. Community programs can raise awareness in schools, workplaces, and vulnerable populations. Healthcare providers should routinely assess patients’ skin health, especially those in high-risk professions. Early identification of symptoms enables timely guidance and treatment. Integrating prevention into occupational health policies and insurance coverage encourages wider adoption of protective measures. Promoting a culture of skin health benefits society by reducing the burden of dermatitis and improving overall wellbeing.