Explore Luxembourg’s Christmas Markets and Winter Beauty
Luxembourg: Europe’s Hidden Gem for December
December is a magical time to visit Europe, with festive markets, holiday lights, and charming winter landscapes. While popular destinations like Paris and Vienna often steal the spotlight, there’s a lesser-known gem in the heart of Europe that deserves your attention—Luxembourg. This small yet stunning country offers a unique blend of history, culture, and holiday charm, making it the perfect destination for a December getaway.
Read Also: How Artists Can Break Out of the Country Music Stereotype
Why Luxembourg is the Perfect December Destination
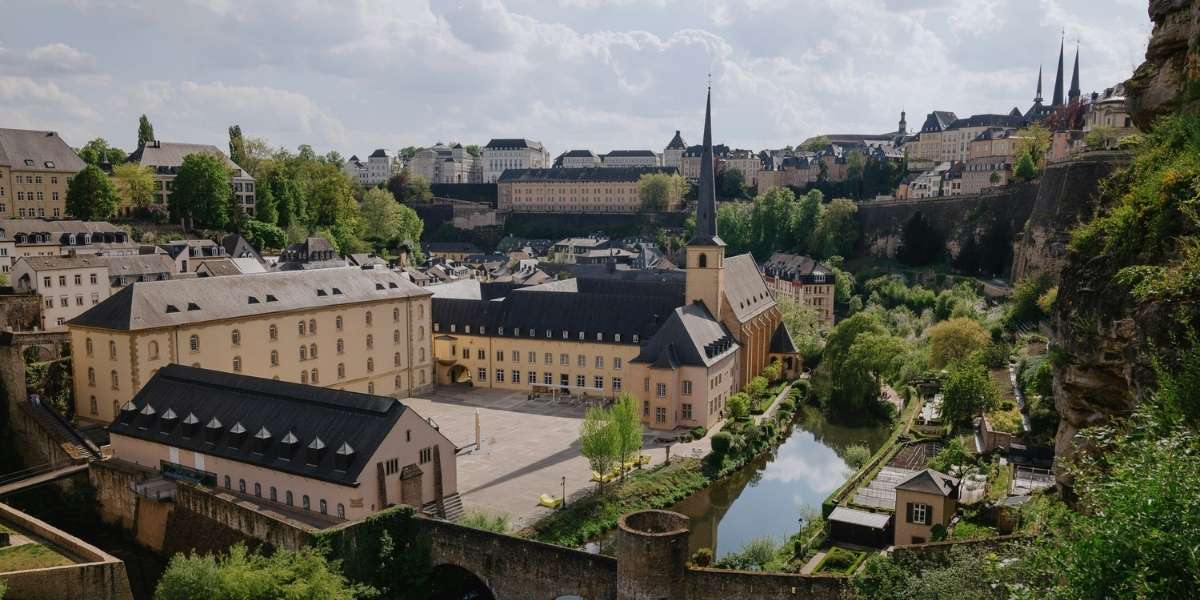
Luxembourg is a country that often gets overlooked in favor of its larger neighbors, but its rich history, vibrant culture, and welcoming atmosphere make it an ideal place to visit during the holiday season. The capital, Luxembourg City, is a UNESCO World Heritage site with a picturesque old town, winding cobblestone streets, and magnificent castles. In December, the city transforms into a winter wonderland, complete with festive markets, twinkling lights, and seasonal events that capture the essence of the holidays.
While Luxembourg might not be the first country that comes to mind when planning a winter vacation, it offers a cozy, intimate experience that’s perfect for those looking to escape the crowds and enjoy a more relaxed pace. Whether you’re strolling through Christmas markets or exploring historic landmarks, Luxembourg delivers a magical holiday experience that’s hard to beat.
The Charm of Luxembourg’s Christmas Markets
During December, Luxembourg City is home to some of the most enchanting Christmas markets in Europe. The Wënzerkrëscht Christmas Market, located in the heart of the city, is a must-see for any visitor. Here, you’ll find beautifully decorated stalls offering handmade crafts, artisanal goods, and delicious seasonal treats. The market is the perfect place to sample local specialties like Gromperekichelcher (fried potato cakes), Kachkéis (cheese pastries), and Bredzäppen (spiced cookies).
One of the most charming aspects of the Luxembourg Christmas markets is their intimate atmosphere. Unlike larger, more crowded markets in other European capitals, Luxembourg’s markets offer a more relaxed experience where you can take your time, enjoy the sights, and truly soak in the holiday spirit. The markets are also set against the backdrop of Luxembourg City’s stunning medieval architecture, making the experience even more enchanting.
Discover Luxembourg’s Rich History and Culture
While Luxembourg is small, it is rich in history and culture, with plenty to explore. December is a great time to visit the country’s many museums, galleries, and historical sites. Start with the Bock Casemates, a series of underground tunnels and fortifications that date back to the 17th century. These UNESCO-listed structures offer a fascinating glimpse into the country’s military history and provide stunning views of the city.
Another must-see is the Grand Ducal Palace, the official residence of the Grand Duke of Luxembourg. The palace, located in the heart of Luxembourg City, is an architectural masterpiece that’s especially beautiful during the winter months, when it’s often adorned with holiday lights. Although the palace is not open to the public during the winter, visitors can admire its grandeur from the outside and explore the surrounding Place Guillaume II, where you can find more holiday festivities.
If you’re a fan of art and culture, Luxembourg also boasts a variety of museums, including the Musée d’Art Moderne Grand-Duc Jean (MUDAM), which features contemporary art exhibitions, and the National Museum of History and Art, which showcases the country’s rich heritage. These cultural experiences provide a deeper understanding of Luxembourg’s history, art, and traditions, making your visit even more enriching.
Luxembourg’s Natural Beauty in Winter
Beyond the charming cityscape, Luxembourg is also known for its natural beauty, which is especially captivating during the winter months. The country is home to lush forests, rolling hills, and picturesque villages that are perfect for exploring on foot or by bike. In December, these landscapes take on a magical quality, with snow-dusted trees and frozen lakes creating a winter wonderland.
The Mullerthal Region, also known as “Luxembourg’s Little Switzerland,” is a particularly stunning area to visit. This region is known for its rocky landscapes, hiking trails, and picturesque villages. While it’s a popular spot for outdoor activities in the warmer months, the winter months offer a serene, peaceful atmosphere that makes it ideal for a quiet getaway.
Why Luxembourg Should Be on Your December Travel List
If you’re looking for a unique European destination to visit in December, Luxembourg should be at the top of your list. From its cozy Christmas markets and festive events to its rich cultural offerings and stunning natural landscapes, Luxembourg offers an unforgettable holiday experience. Whether you’re wandering through the charming streets of Luxembourg City, exploring its historical landmarks, or enjoying its beautiful winter scenery, you’ll find that this hidden gem has a special kind of magic during the holiday season.
Read Also: Discover the Evolution of Hybrid Music Genres
So, if you’re seeking a holiday destination that’s off the beaten path yet filled with charm and beauty, Luxembourg is the perfect choice for your next December adventure.