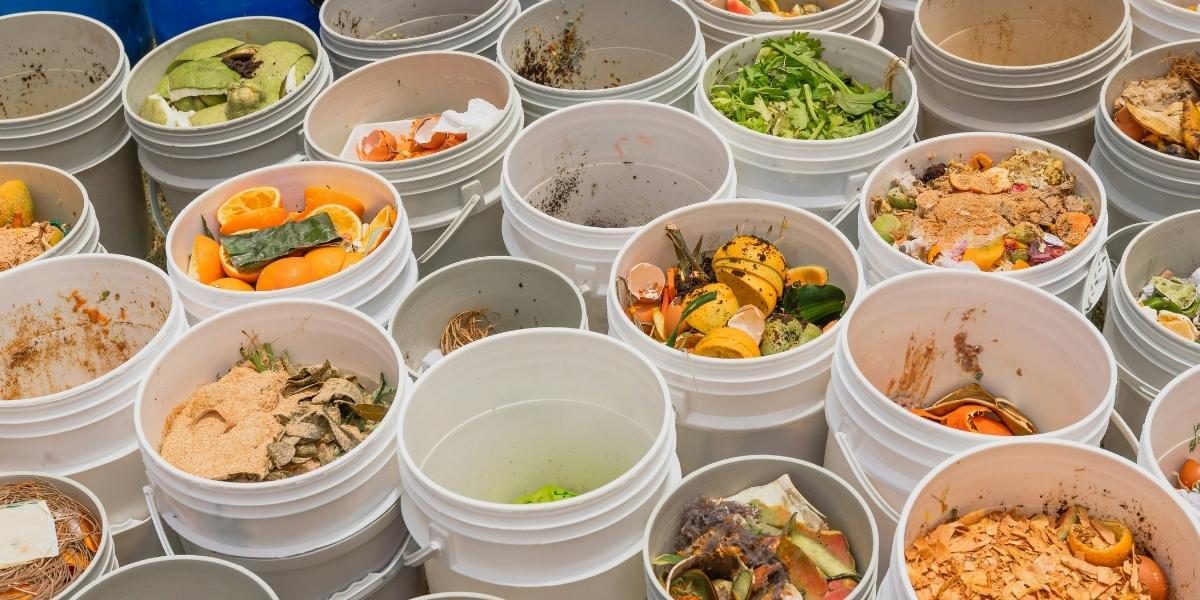
The topic of food waste reduction is gaining significant attention as businesses and consumers alike face the environmental and economic consequences of discarded food. Over one-third of all food produced globally is wasted, with large-scale food systems playing a major role. Understanding how these systems address this issue reveals important strategies that can promote sustainability, improve efficiency, and reduce costs across the supply chain.
Read Also: The Impact of Artist Advocacy on Society’s Awareness and Action
Why Is Food Waste Reduction Crucial?
Food waste includes losses at production, processing, distribution, and retail stages. This waste not only represents a lost opportunity to feed people but also contributes heavily to environmental problems. When food is discarded, all the resources used in its production—water, energy, labor, and land—are wasted as well.
Large-scale food waste is responsible for a substantial share of greenhouse gas emissions. When wasted food decomposes in landfills, it releases methane, a gas far more potent than carbon dioxide. Efforts toward food waste reduction can therefore significantly lower a business’s carbon footprint and contribute to climate change mitigation.
In addition to environmental impacts, food waste results in major financial losses. Companies face costs related to purchasing, handling, and disposing of food that never reaches consumers. Business leaders recognize that reducing waste not only supports corporate responsibility but also improves profit margins.
How Do Food Systems Approach Waste Reduction?
Many organizations are adopting a combination of technological, operational, and behavioral strategies to tackle food waste. Advances in supply chain management and data analytics allow businesses to predict demand more accurately and minimize overproduction.
For example, smart inventory systems help retailers track product freshness and optimize stock levels. This technology reduces the risk of unsold perishable goods spoiling before sale. Similarly, manufacturers use improved processing techniques to extend the shelf life of products.
Another significant approach involves collaborating with suppliers and distributors to improve logistics. Reducing delays and maintaining proper storage conditions can preserve food quality and reduce spoilage during transport.
Companies are also revising portion sizes and packaging to align better with consumer preferences and minimize leftover waste. Consumer education campaigns encourage responsible purchasing and disposal habits, complementing waste reduction efforts.
What Role Does Innovation Play in Food Waste Reduction?
Innovation is central to accelerating food waste reduction. New technologies like artificial intelligence and machine learning analyze sales patterns and predict fluctuations, helping businesses respond quickly to changes in demand.
Biodegradable and smart packaging materials are emerging to extend freshness and alert consumers when products are nearing expiration. These innovations improve transparency and reduce unnecessary disposal.
Food recycling and upcycling represent additional innovative strategies. Some companies transform food byproducts or imperfect produce into new products such as animal feed, bioenergy, or packaged snacks. This practice reduces waste while creating new revenue streams.
Industry-wide initiatives and certifications also encourage companies to set clear goals and share best practices. Such frameworks foster accountability and collaboration across the supply chain.
How Does Food Waste Reduction Benefit Society?
The benefits of reducing food waste extend beyond businesses to society at large. By minimizing waste, more food becomes available to address food insecurity and hunger.
Several companies partner with food banks and charities to donate surplus edible food, providing nutritious options to vulnerable populations. This collaboration strengthens community ties and improves social outcomes.
Environmental benefits are profound as well. Lower waste means fewer resources consumed and reduced pollution, helping conserve ecosystems and biodiversity.
Consumers increasingly demand sustainability, and companies that actively reduce food waste enhance their reputation and customer loyalty. This positive feedback loop motivates ongoing improvements and innovation.
What Challenges Remain in Reducing Food Waste?
Despite progress, significant challenges persist. Complex supply chains, varying regulations, and logistical hurdles can impede waste reduction efforts. Coordination among multiple stakeholders is often difficult.
Economic pressures sometimes lead businesses to prioritize short-term gains over sustainable practices. Smaller companies may lack the resources to invest in advanced technology or waste management systems.
Moreover, consumer behavior plays a critical role. Even with improvements, food waste at the consumer level remains high, often linked to confusion over expiration dates and portion control.
To overcome these barriers, ongoing commitment, education, and policy support are necessary. Encouraging transparent reporting and creating incentives for waste reduction can drive further change.
Read Also: Understanding the Surfer’s Quest for Bigger Waves Across the Sea
What Does the Future Hold for Food Waste Reduction?
Looking forward, food waste reduction efforts are likely to advance through continued innovation, collaboration, and regulation. As technology becomes more accessible, even smaller players will gain tools to reduce waste effectively.
Sustainability will remain a core priority for businesses seeking to meet environmental targets and respond to consumer expectations. Circular economy models, which treat waste as a resource, will gain traction.
Governments and international organizations are expected to implement stronger policies and standards to support waste reduction goals. Transparency and data sharing will improve accountability.
Overall, the evolving food sector offers opportunities to build a more efficient, responsible, and equitable food system that benefits people and the planet.