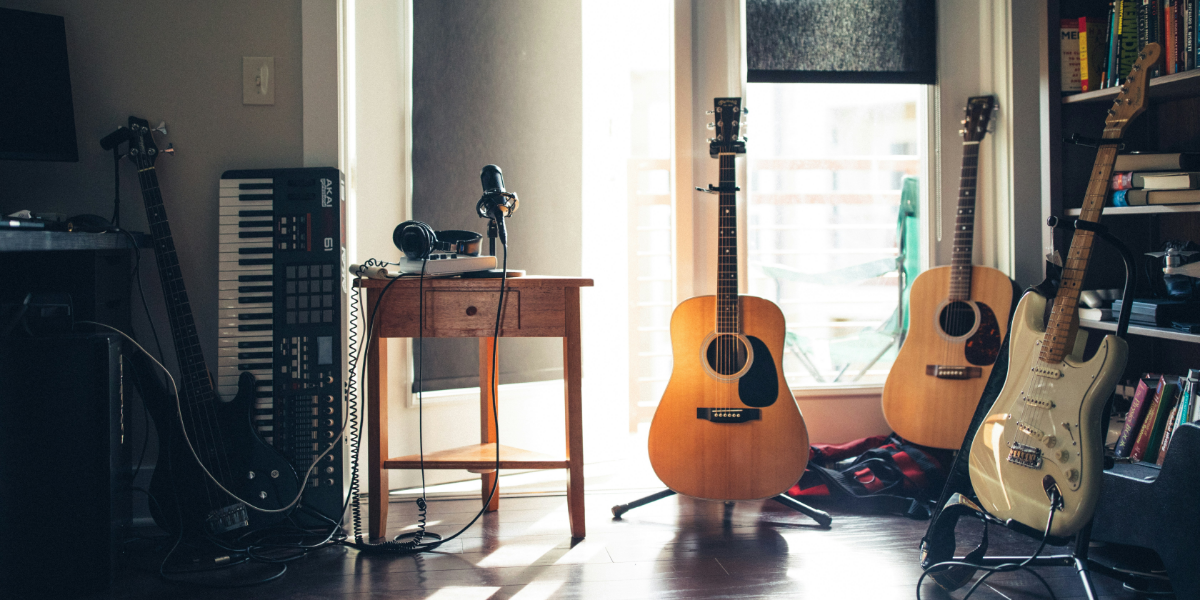
Recording guitar tracks is an exciting and rewarding process, whether you’re laying down riffs for a demo or tracking parts for a full album. Achieving professional, high-quality guitar recordings requires a blend of technical skills, creativity, and careful preparation. This guide provides essential tips and techniques, from setting up your space to perfecting your mix, to help you capture the ideal guitar sound.
Setting Up Your Recording Space
The recording environment significantly affects the clarity and quality of your guitar tracks. A well-prepared space helps minimize unwanted noise and reflections, creating a cleaner, more professional sound.
Acoustic Treatment
Choose a room with minimal sound reflections to reduce reverb that can make recordings sound muddy. Use acoustic panels on walls and corners to absorb unwanted reflections. If you’re on a budget, heavy curtains or blankets can also help absorb excess sound and improve clarity. Treating your room acoustically prevents the recording from sounding “echo-y,” giving your guitar tones a more defined sound.
Isolation
Isolation is crucial, especially in home studios. To prevent interference from other sounds, isolate the guitar amp using isolation shields or microphone baffles. Placing the amp in a separate room or closet can help if you have the space. By reducing ambient noise, isolation allows you to capture the purest sound from your guitar and amp.
Selecting the Right Equipment
Using the right recording equipment is essential for capturing the nuanced tones and textures of your guitar. Good-quality microphones and audio interfaces enhance your ability to produce a clean recording.
Microphones
Choosing the right microphone affects the overall tone and detail of your recording. Dynamic microphones, like the Shure SM57, are widely used for electric guitar amps due to their durability and ability to handle loud sounds without distortion. This microphone captures a focused mid-range sound that works well with electric guitars.
Condenser microphones are typically used for acoustic guitars as they capture more detail and high-frequency clarity, producing a natural, accurate tone. Experiment with microphone placement to achieve the sound you want. For instance, close-miking a dynamic mic near an amp provides a direct, punchy sound, while positioning a condenser mic slightly further away from an acoustic guitar captures a fuller, richer tone.
Audio Interface
A quality audio interface is essential to transfer the guitar signal to your computer. Choose one with low-latency monitoring and multiple inputs, especially if you’re recording multiple mics. If using condenser mics, ensure your interface has phantom power, as these mics require external power. A good interface ensures sound quality and minimizes latency, making it easier to monitor your recording in real time.
Dialing in Your Guitar Tone
Achieving the desired tone at the source saves time in post-production and ensures a solid foundation for the recording.
Amplifier Settings
Spend time adjusting amplifier EQ settings, gain, and effects to shape your sound. Small changes to the bass, mid, and treble levels can dramatically alter tone. Use effects pedals to add variety, such as reverb for depth or overdrive for grit. Experimenting with EQ and effects helps you find a tone that best suits the track and reduces the need for excessive editing later.
Guitar Setup
Ensure your guitar is properly tuned and intonated. Tuning issues can be difficult to fix post-recording and can detract from the quality of the track. Experiment with pickup combinations to explore different tonal options. For instance, the bridge pickup may provide a sharper, more aggressive tone, while the neck pickup gives a warmer, rounder sound, allowing you to tailor the guitar sound for each section of the song.
Recording Techniques
Various recording techniques can bring out the best qualities of your guitar sound, adding depth and dimension to the recording.
Close Miking
Close miking involves placing a microphone directly near the amp’s speaker cone, usually an inch or two away. Positioning the mic slightly off-axis can create a warmer tone. This technique is commonly used for electric guitars as it produces a direct and powerful sound with minimal ambient interference, making it suitable for capturing detail and focus.
Room Miking
Using a room mic adds depth and natural ambiance by capturing the sound of the room. Positioning a microphone further from the amp or acoustic guitar creates a blend of direct and reflected sound. Adjusting the room mic’s distance allows you to control the balance between direct and ambient sound, resulting in a fuller, more immersive recording.
Post-Recording Processing
Post-production techniques refine your recording and give it a polished, professional quality.
Editing
Use editing software to clean up the recording by removing background noise and correcting timing issues. Reverb, delay, and compression can enhance depth and consistency. Be mindful not to overuse effects; subtlety is key to maintaining a natural sound that doesn’t overpower the guitar’s original tone.
Mixing
Balancing guitar tracks within the mix is crucial. Use EQ to carve out space, especially by adjusting frequencies that may clash with other instruments. Panning rhythm guitars left and right and keeping lead parts centered can create a balanced, spacious soundscape. Adjusting each track’s volume and EQ ensures that the guitar complements other instruments without overpowering the mix.
Conclusion
Recording guitar tracks combines technical skill with a creative approach. By preparing your space, selecting the right equipment, and refining your recording techniques, you can capture clean, professional-quality guitar recordings. Whether you’re an experienced musician or an enthusiast recording at home, these tips and techniques offer a solid foundation for achieving the ideal guitar sound. With practice, you’ll develop a recording style that showcases your unique sound, enhancing the quality and impact of your music projects.
Published by: Khy Talara